Introduction
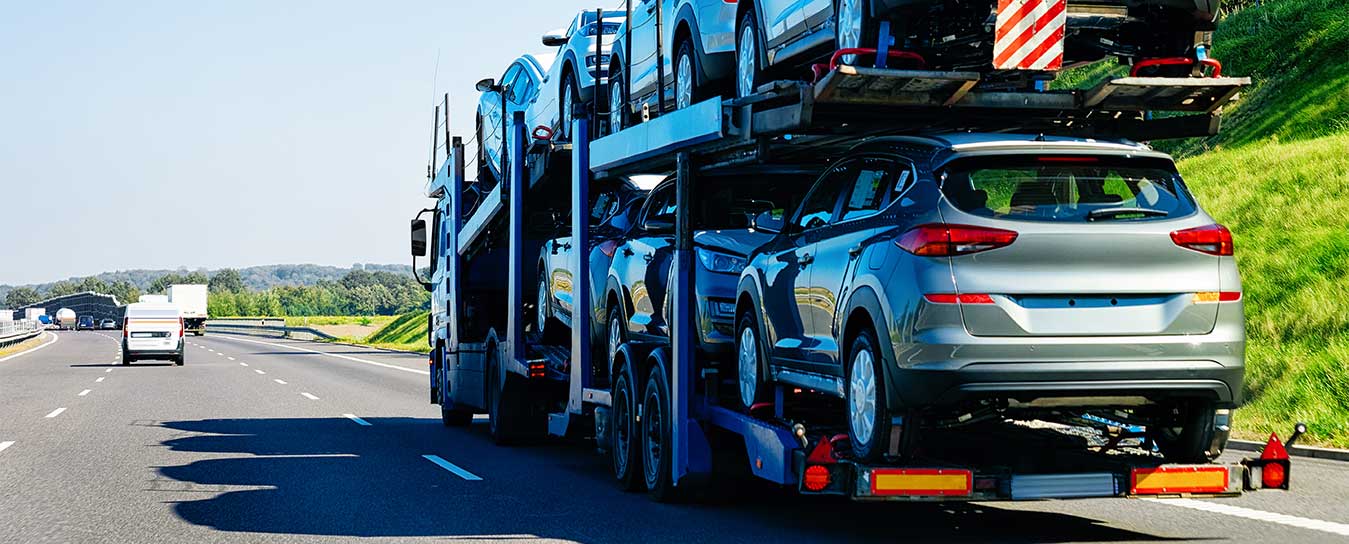
Car importing into Canada is a fulfilling experience for those who want to import a car to Canada or take advantage of better offers from other markets. However, the importer must meet some challenges in clearing the goods. Meeting the compliance requirements, paperwork, and costs and knowing the challenges enhance smooth imports. Some of the problems associated with importing cars into Canada are elaborated with the recommended remedies.
1: The main reason is that the client wants to conform to Canadian Standards.
This is among the hardest decisions to make when import a car to Canada because the vehicle has to meet Canadian safety and emission standards. Canadian rules concerning automotive safety, emissions, and equipment may greatly vary from those of the United States, Japan, or any other country.
Solution:
Certify the information with the Canadian Vehicle Regulations (CVR) provided by Transport Canada before an individual imports a car. This ranges from guaranteeing that the car complies with the Canadian Motor Vehicle Safety Standard (CMVSS) and the US Environment Protection Agency (EPA) emission standards. One must know whether the vehicle must be modified to meet light, bumpers, or emissions control systems requirements. You should go to a registered importer or contact a professional service provider that provides car import services so that your car can fully meet all the requirements.
2: Paperwork and Documentation
The formalities associated with importing a car to Canada may consist of many documents, including customs declarations, ownership documents, and import permissions. Insufficient or wrong paperwork slows the process, and fines or car rejection are possible.
Solution:
To prevent delays, make sure you have all the necessary documents, including:
- Proof of ownership (Receipt of sale/invoice/vin, registration /title/ legal ownership documents).
- Existing Import Form (The CBSA import form 1, the import declaration).
- Customs Declaration and any tariffs or taxes that are required to be paid.
- Files of Safety and Emissions Compliance (as appropriate). Be sure to bring copies of your insurance and passport as well. A customs broker will save time when the necessary paperwork is checked, and all documents are submitted properly.
3: Import Duties and Taxes
When a car importing to Canada, there are normally several costs that one has to meet. These are the import duties, taxes, and fees. These additional costs may include extra expenses on some features of the car and may considerably increase the general price of the auto.
Solution:
This is why it is important to understand these costs before importing. Customs on imported vehicles vary, with rates ranging from 6% to 10% of the car’s value, depending on the vehicle’s home country. Plus, depending on the import province, the customer will be subject to paying for Goods and Services Tax (GST) or Harmonized Sales Tax (HST). Some provinces may incur extra fees for registration, inspection, or licensing services.
Some of these costs can be avoided by obtaining a car from a country with a free trade agreement with Canada. For example, the Canada-United States-Mexico Agreement (CUSMA) addresses specific duty-free vehicles from the US or Mexico.
4: Vehicle Inspection and Modification
Automobiles imported into Canada must be examined to ensure they conform to the country’s existing standards. Different vehicles may require modifications depending on the specifications set, making the process expensive and long.
Solution:
Prepare for at least a general check-up of your vehicle as soon as it arrives in Canada. If the vehicle requires changes, consult experts familiar with Alberta’s standards for automobile modifications. This may include correcting the speedometer, replacing bumpers, or installing an approved immobilizer system. At other times, it may be necessary to add a catalytic converter to conform to the set environmental requirements.
5: Registration and Licensing
After inspecting your vehicle, you must register it with the appropriate provincial or territorial government motor vehicle agency. This process can sometimes be a bit puzzling because the requirements differ from one geography to another.
Solution:
Ensure you have clarified the registration process in your province or territory of the country. Typically, you must show the deed of title, identification card, and periodic inspection receipt of the car. The process may also require you to provide documents related to compliance with emission standards and registration fees.
Conclusion
Importing a car to Canada requires a thorough understanding, careful planning, and proper preparation. With the above tips and tricks, you can minimize the challenges of bringing your car into Canada. By ensuring your vehicle meets Canadian standards, organizing all necessary documents, and accounting for additional costs, you will streamline the process and avoid unnecessary complications. In addition, professionals such as customs brokers, registered importers, and vehicle compliance specialists can significantly simplify the process, making it much more manageable and less stressful. Consequently, importing a car to Canada becomes a straightforward task, provided you take the necessary steps and ensure the proper preparations are in place.
You’re not alone if you’re still unsure about the car importation process or have specific questions! Many individuals face similar challenges when bringing vehicles into Canada. I regularly share insights, tips, and real-life experiences on Quora to help make the process easier for everyone.